Optical Illusions : Think you’ve got sharp eyes? The humble spot-the-difference challenge has evolved far beyond simple entertainment, with Australian researchers now using optical illusions to train artificial intelligence systems and revolutionize how we understand human perception.
Recent breakthroughs from Charles Sturt University are positioning Australia at the forefront of quantum-inspired AI development, while international studies reveal that training with optical illusions can dramatically improve visual processing skills.
Australian Researchers Lead Global Innovation in Optical Illusion AI
Dr Ivan Maksymov, Principal Research Fellow at Charles Sturt University’s Artificial Intelligence and Cyber Futures Institute, has created a revolutionary neural network that can perceive optical illusions much like humans do. His quantum-inspired approach represents a fundamental shift in how artificial intelligence processes visual information, moving beyond simple pattern recognition to understanding the ambiguous nature of human perception.
Using a phenomenon called “quantum tunneling,” Maksymov’s neural network successfully simulated human perception of famous illusions like the Necker cube and Rubin’s vase. This breakthrough challenges traditional approaches to machine learning and opens new possibilities for creating AI systems that think more like humans.
Applications for Australian Aviation Industry
The research holds particular promise for the Australian Airline Pilot Academy (AAPA) at Wagga Wagga, where the neural network could help train pilots to handle visual illusions encountered during flight. Pilots often face dangerous optical illusions, especially when flying through clouds or over water, where distinguishing up from down becomes critical for safety.
“This same Neural Network Model could be advantageous for psychologists, behavioural scientists, vision scientists, machine learning experts, developers of virtual reality systems and video games, as well as by trainers of astronauts,” Dr Maksymov explained.
The 90-Second Challenge: Testing Your Visual Perception
Before diving deeper into the science, let’s put your observation skills to the test. The classic spot-the-difference challenge remains one of the most effective ways to measure visual perception abilities. Finding three differences between seemingly identical images in just 90 seconds separates casual observers from those with exceptional perception.
Most people can identify one difference quickly, but locating all three within the time limit requires both speed and accuracy. Rushing leads to overlooked details, while overthinking wastes precious seconds. This delicate balance makes these challenges excellent brain training tools.
What Happens in Your Brain During Visual Challenges
Recent research from the University of Tokyo reveals that rhythmic waves of brain activity cause us to see or not see complex images that flash before our eyes, with attention fluctuating six to eight times per second in what scientists call “theta rhythms”. Understanding these neural patterns helps explain why some people excel at spot-the-difference challenges while others struggle.
When encountering these puzzles, your visual cortex kicks into high gear, creating what scientists call “saccadic movements” as your eyes rapidly dart between images hunting for inconsistencies. Your working memory juggles multiple visual elements simultaneously, representing a significant mental workout that strengthens neural pathways related to focus and attention.
Medical Experts Excel at Visual Illusions
Groundbreaking research from UK universities, including the University of East Anglia, has discovered that medical imaging experts are remarkably adept at solving optical illusions and judging object sizes accurately. This finding challenges the long-held belief that susceptibility to optical illusions is fixed and unchangeable.
The study tested 44 radiographers and radiologists against 107 non-experts, revealing that medical professionals’ intensive visual training made them significantly less susceptible to visual illusions. This research proves that perceptual skills can be developed through practice, opening new possibilities for brain training applications.
Training Your Brain to Resist Illusions
Scientists now believe that people can learn to “unsee” optical illusions through targeted training. The key lies in understanding how context affects perception. Professional radiologists develop heightened attention to detail through years of analyzing medical images, making them less likely to fall for visual tricks.
Cultural differences also play a fascinating role in illusion perception. Research shows that East Asian perception tends to be more holistic, taking everything into account, while Western perception focuses more on central objects, leading to different levels of illusion sensitivity.
Breakthrough Animal Research Reveals Universal Patterns
Recent studies from the University of Leipzig demonstrate that ungulates like sheep, llamas, and goats also fall for optical illusions, suggesting these animals share similar neural wiring for vision with humans. This research provides crucial insights into when and why falling for optical illusions evolved in animals, helping scientists understand the fundamental nature of visual perception.
Business Applications and Cognitive Benefits
Modern research reveals that training with optical illusions can significantly improve business performance by enhancing visual literacy and problem-solving abilities. Visual literacy encompasses our ability to interpret and derive meaning from visual information, skills that prove invaluable when analyzing complex data, marketing reports, or customer behavior patterns.
Popular optical illusions like the Ebbinghaus illusion challenge our brains by presenting context in misleading ways, and practicing our ability to see past this misleading context trains our brains to be more accurate when interpreting images.
Strategies for Success in Spot-the-Difference Games
Professional puzzle masters employ systematic techniques that anyone can learn. The quadrant approach involves dividing each image into sections and methodically comparing corresponding areas, preventing the random searching that often leaves differences undiscovered.
Another effective strategy involves relaxing your focus slightly, allowing peripheral vision to detect inconsistencies. Sometimes your brain notices differences faster through passive observation rather than active searching. Experienced puzzlers typically start with faces and focal points, as designers frequently hide modifications in high-interest areas.
Digital Age Applications
Today’s technology offers countless resources for visual puzzle enthusiasts. Dedicated applications provide daily challenges with increasing difficulty levels, while websites specializing in cognitive development feature extensive libraries with scoring systems to track improvement over time.
For maximum benefits, applications combining time tracking with difficulty progression provide the most structured approach to improving visual perception skills. These digital tools make brain training accessible to anyone seeking to enhance their cognitive abilities.
The Future of Optical Illusion Research
Dr Maksymov’s quantum-inspired approach represents just the beginning of a new era in understanding visual perception. His research promises applications in psychology, psychiatry, pilot training, and virtual reality development, while the ability to conduct complex neural research in weeks rather than years opens unprecedented opportunities for rapid advancement.
The intersection of quantum mechanics and artificial intelligence through optical illusion research positions Australia as a global leader in next-generation AI development. These advances could revolutionize everything from medical diagnosis to space exploration, where understanding visual ambiguity becomes critical for human safety and success.
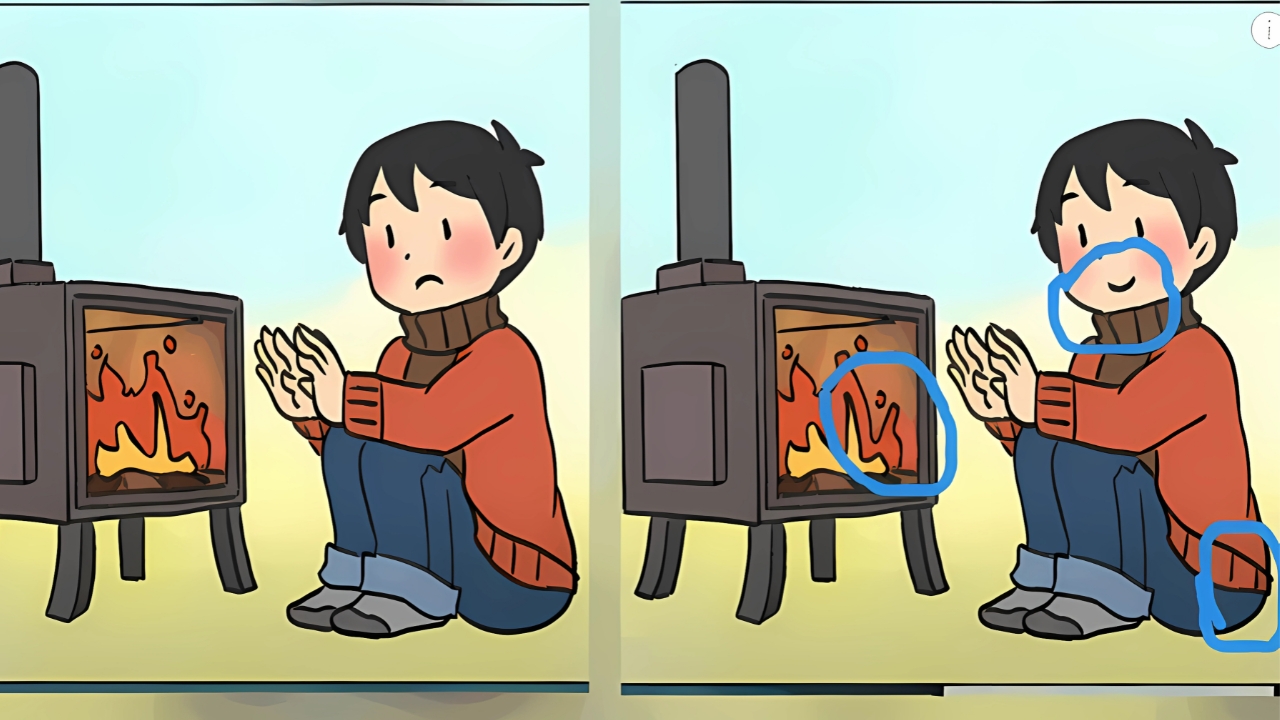
Optical illusion Answer

Frequently Asked Questions
Can optical illusion training improve everyday vision skills? Yes, regular practice with visual puzzles strengthens attention spans, enhances pattern recognition, and improves visual discrimination abilities that transfer to real-world tasks requiring careful observation.
Why are some people naturally better at spot-the-difference challenges? Individual differences in visual processing speed, attention control, working memory capacity, and cultural background all contribute to performance variations in optical illusion perception.
How long does it take to see improvements from brain training with illusions? Most people notice enhanced focus and visual processing within 2-3 weeks of regular practice, with significant improvements typically visible after consistent training over several months.
